Summary
The NHS green estate (trees, woodland, grass, and other green infrastructure) is wide and varied, and its stakeholders have competing priorities for use and management.
The NHS in England is organised into 42 Integrated Care Systems (ICS), each with their own strategy and Green Plan. The Green Plans focus on reaching net zero through consideration of energy, waste, food, and biodiversity. In the next round of Green Plans there will be a focus on providing space for nature and adapting the NHS estate to climate change.
Woodland and tree planting is already taking place on the NHS estate, with some targeted planting to enhance tree connectivity and air pollution removal. Trees and woodland have the potential to provide a range of benefits, also known as ecosystem services, including reducing health inequality, reducing temperatures on hospital wards, contributing to achieving net zero, providing access to greenspace in and around hospital sites, and improving the health and wellbeing of people.
This work explores options for quantification and valuation of some of the ecosystem services provided by woods and trees on the NHS estate.
Research Objectives
The purpose of this study was to explore options for valuation of ecosystem services provided by trees and woodland on the NHS estate. This was a pilot study designed to:
- test the applicability of existing ecosystem service quantification and valuation methods to the NHS estate
- illustrate the insight that can be gained from the process
- investigate options for development of quantification methods for the NHS estate
- make recommendations for the roll-out of the methodology to the wider NHS estate
Findings and Recommendations
We used a logic chain approach to quantify and value ecosystem services provided by trees and woodland on four NHS sites.
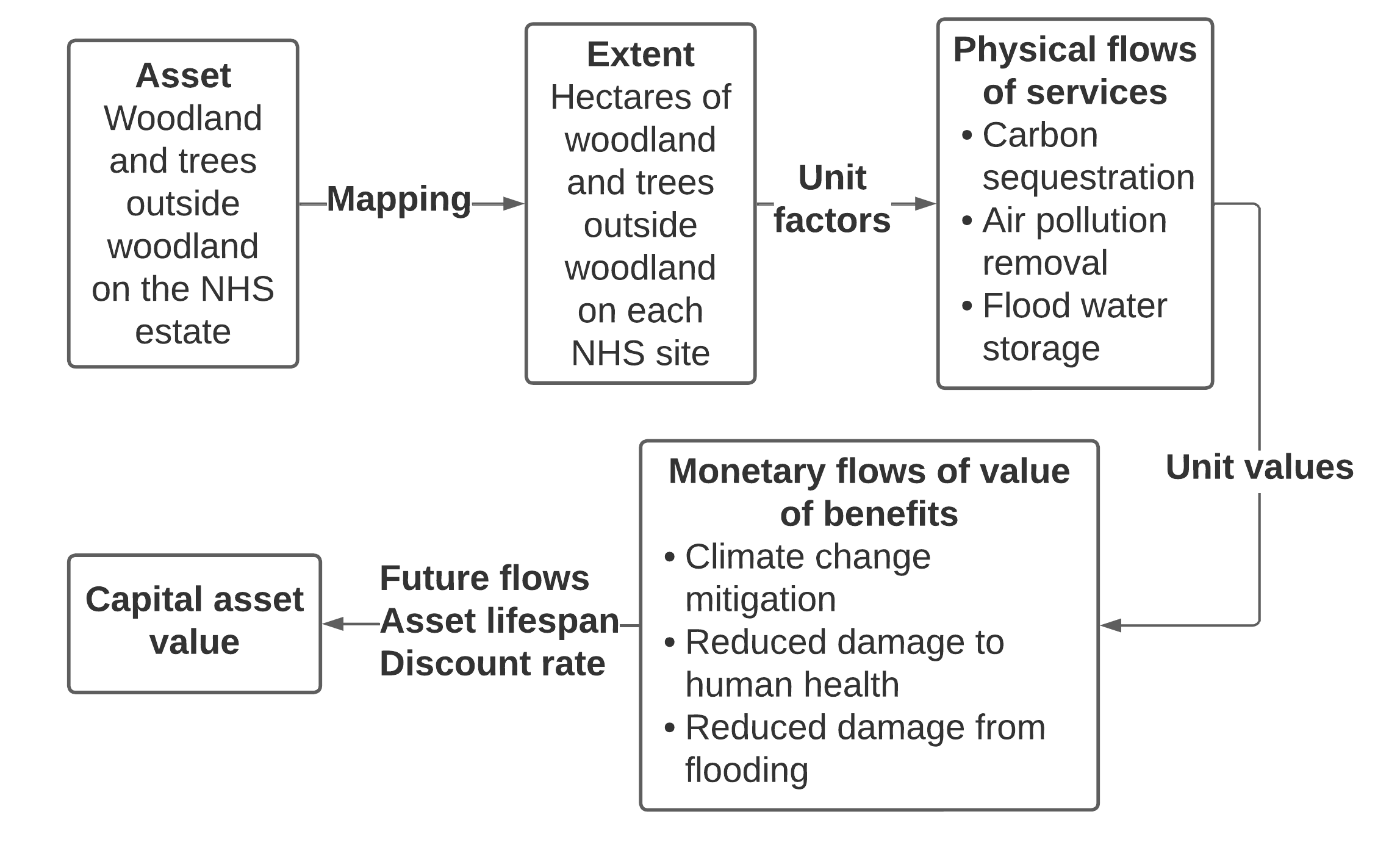
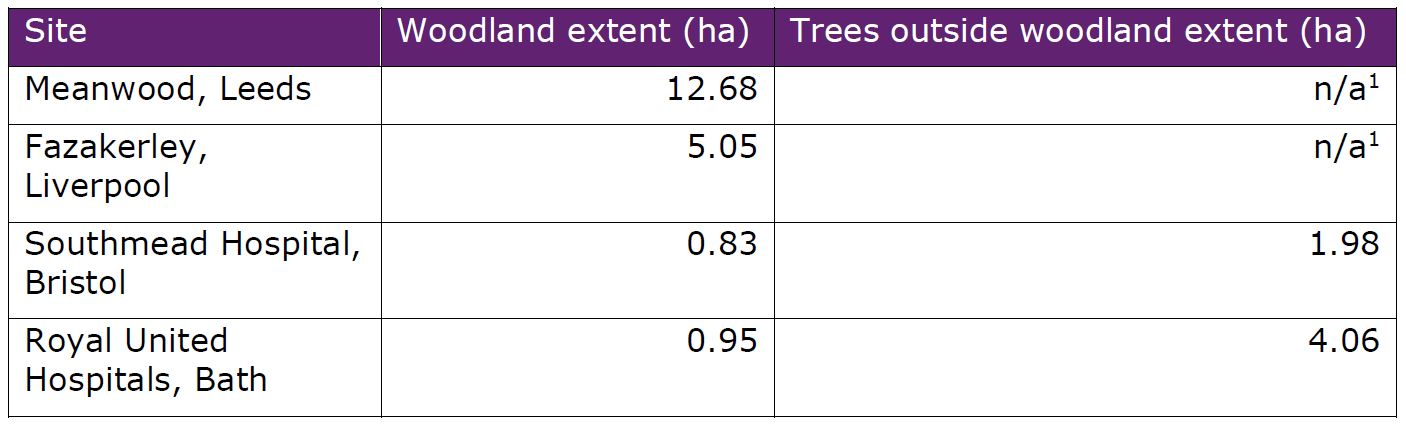
We used i-Tree Canopy and hand mapping in a Geographic Information System (GIS) to quantify the extent of woodland, and trees outside woodland, on four NHS estates:
- Meanwood, Leeds
- Fazakerley, Liverpool
- Southmead Hospital, Bristol
- Royal United Hospitals, Bath
Table 1: Extents of woodland and trees on four NHS sites
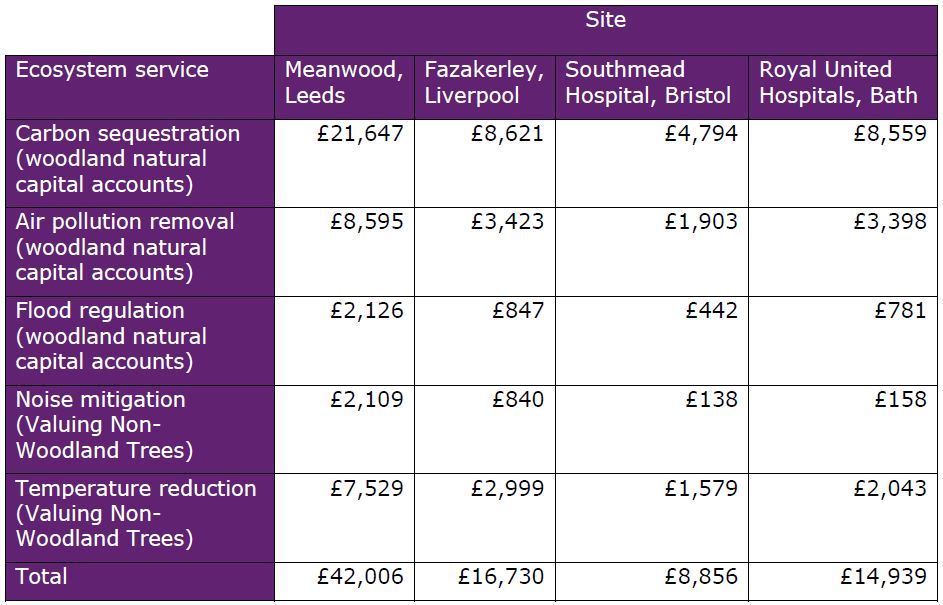
We applied methodologies from the urban and woodland natural capital accounts, and from Valuing Non-Woodland Trees, to estimate ecosystem service provision by the woodland and trees outside woodland on each site.
Table 2: Values of annual flows of ecosystem services from trees and woodland on four NHS sites
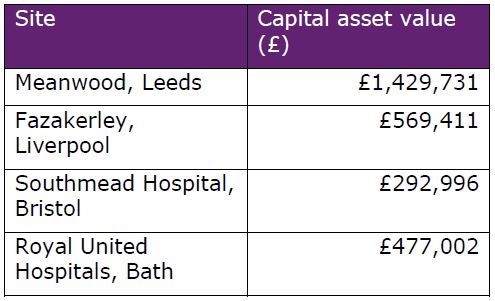
We used the 100-year present value approach to estimate the capital asset values of ecosystem service provision by trees and woodland on each site.
Table 3: Estimated capital asset values of trees and woodland on four NHS sites
We recommend quantification of trees and woodland on the wider NHS estate and application of the woodland and urban natural capital accounts methodologies.
The full pilot study report is available to download below.

