Summary
Overview
In order to gain a better understanding of the effects of air pollution, climate change and other stress factors affecting UK forest ecosystems, long-term intensive monitoring plots were established in 1995 under the convention on long range air Pollution (CLRTAP). Ten plots covered three important tree species Sitka spruce, Scots pine and Oak. In 2002 the number of plots was extended to include Beech and Norway spruce. These plots formed part of a Europe-wide ICP forests ‘Level II’ programme network.
Map showing geographic distribution of Level II plots in Europe
Click here for a map and list of all Level II plots in Britain
This research complements large-scale surveys of tree health established in Britain by the Forestry Commission, and in many European countries, during the 1980s.
The intensive monitoring programme is a vital resource to detect environmental change in UK forests and to provide the means of explaining changes in forest growth. It has produced valuable data, and considerable insight into the dynamic nature of UK forest ecosystems.
Each plot is 0.5 ha in area and contains a mensuration sampling plot of 0.1ha used to measure growth factors.
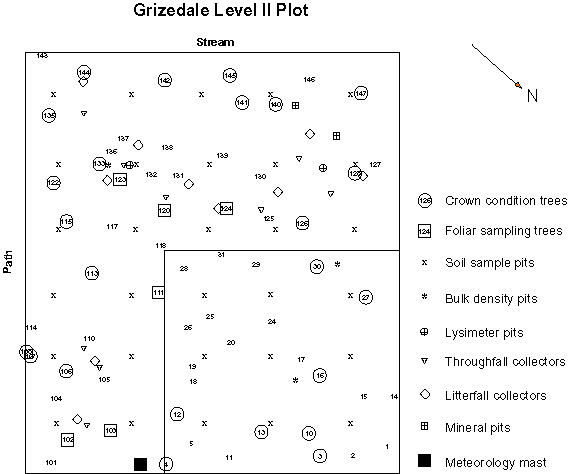
Plots were established in working forests under normal forest management, so data also document change due to management practices. Data from these plots are being used to support other environmental research programmes, and also to provide information for wider Forestry Commission objectives, namely the protection of Britain’s forests and woodlands, sustainability, and soil and water quality.
Parameters measured and frequency of assessment
The intensive forest monitoring network is supported by detailed measurements of a wide range of variables.
Summary of data collection across all Level II forest monitoring sites
Research Objectives
- Characterise the UK forests in terms of their relationship to other European monitoring sites.
- Understand the fate of atmospheric pollutants in a range of managed forest ecosystems; i.e. their accumulation, distribution, patterns of release and leaching.
- Identify cause-effect relationships which explain the extent to which air pollution and other abiotic (e.g. inter-annual variation in climatic conditions, storms, fire) and biotic (e.g. pest and diseases, newly emerging diseases) stress factors contribute towards observed variations in forest condition.
- Review the likely impact of future scenarios of climate change, air pollution and other abiotic and biotic stress factors on managed forest ecosystems.
- Contribute to assessments of net carbon sequestration by European forests. Also, contribute to assessments of the global carbon balance.
- Determine critical levels/ loads of atmospheric pollutants (SO2, NO2, NH3 and heavy metals such as Cu, Cr, Zn, Cd, Ni and Pb) for managed forests in the UK under current and predicted climatic conditions.
- Develop and test indicators that can be used to assess the long-term sustainability of forest ecosystems and shifts in biodiversity.
Latest Update
Since 1995, 10 permanent intensive monitoring Level II plots have been installed in Britain in accordance with EU protocols. These represent three important forest species:
- Sitka spruce (Picea sitchensis (Bong.) Carr)
- Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.)
- Oak (Quercus spp.).
An additional 10 plots were added between 2002 and 2008, including a further two important forest species: beech (Fagus sylvatica) and Norway spruce (Picea abies).
Long term monitoring is intended to continue into the next crop rotation.
General Content
What’s of interest
Alice Holt Research Forest – International links
Patterns of mast fruiting of common beech, sessile and common oak, Norway spruce and Scots pine in Central and Northern Europe. (2016) Forest Ecology and Management
Tree mineral nutrition is deteriorating in Europe.(2014) Global Change Biology
Pitman, R., Vanguelova, E.I. and Benham, S. (2010). Effects of phytophagous insects on the nutrient concentrations and fluxes through forest stands in the UK Level II network. Science of the Total Environment 409 (1): 169-181.
Ten Years of Intensive Environmental Monitoring in British Forests. Forestry Commission Information Note 88
Downloads
ICP Forests
Contact
Caitlin Lewis – caitlin.lewis@forestresearch.gov.uk
Funding & Partners
The programme was jointly funded by the Forestry Commission and the European Union and is now funded solely by the Forestry Commission.




