This paper summarises the results of Forest Research’s citizen science canopy cover webmap.
Tree canopy cover was measured by contributors to the project in 5,749 urban wards in the UK using a random sample, manual image classification tool called i-Tree Canopy.
The area-weighted mean canopy cover across urban areas in the UK was found to be 17.3%. There were variations in canopy cover across UK countries, regions, towns and cities. The highest regional canopy cover is found in South Wales (19.2%) and the south-east of England (22.1%). The lowest regional canopy cover is found in Northern Ireland (11.8%).
Low canopy cover was found to be associated with deprivation in England, and with high population density in England and Wales.
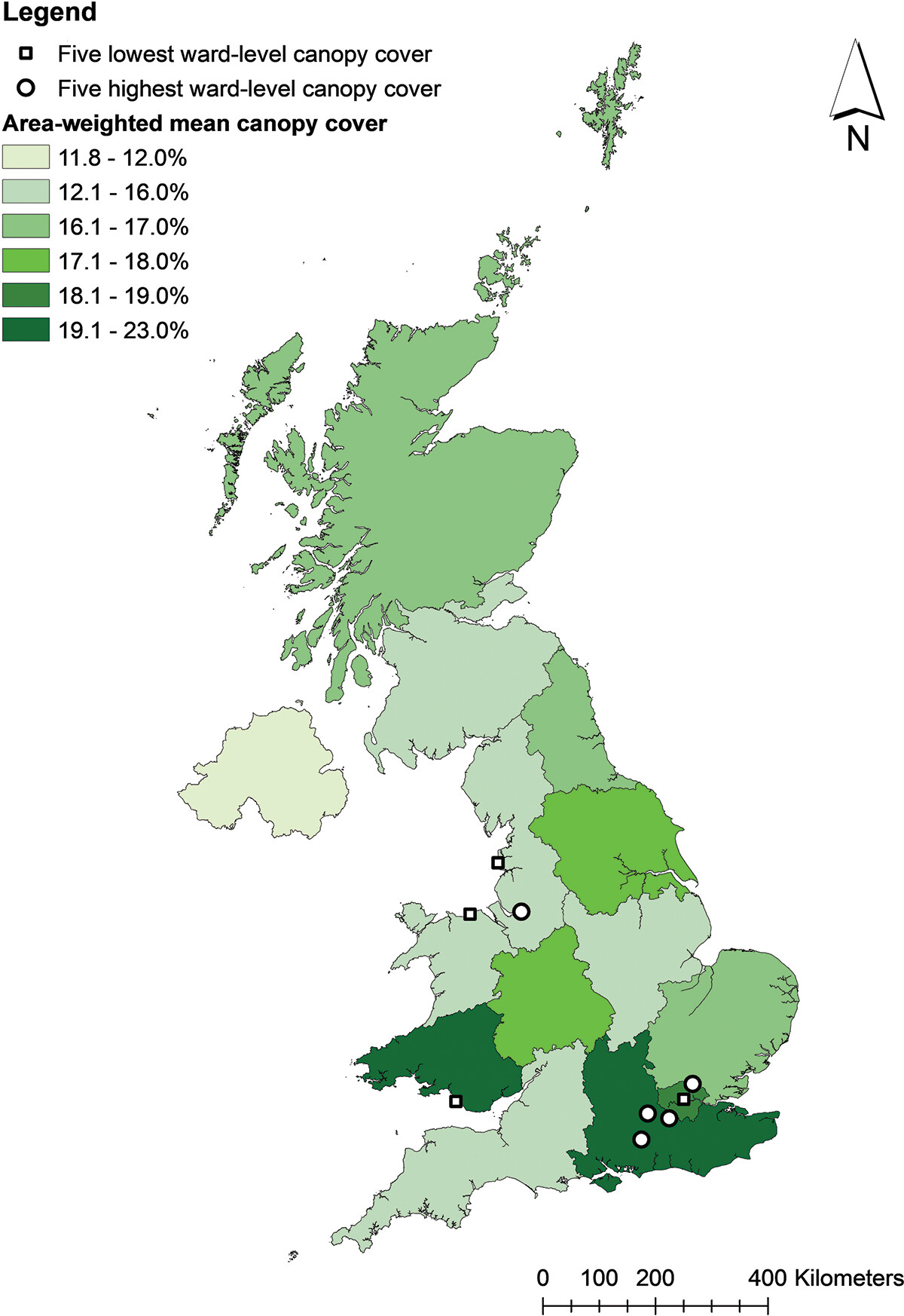
The tree canopy cover of most wards fell short of the suggested canopy cover target of 20%, and tree canopy cover is found to be inequitably distributed across all urban areas in the UK.
In future, UK-wide and national analyses could progress to models which characterise longitudinal patterns in urban green infrastructure, and identify drivers for high and low canopy cover. Optimum and achievable rates of change of canopy cover could be identified, for effective and sustainable benefit delivery.
