Tree Species Guide for UK Agroforestry Systems
This tree species guide, developed in partnership with the University of Reading following a rapid review of literature, databases, and…
Woodland owners and managers are being asked to take part in an important new research project aiming to monitor the health of oak trees across the UK.
Find out more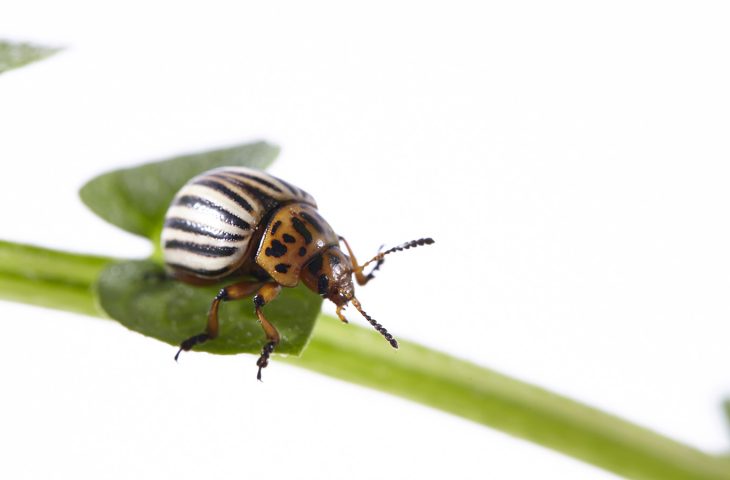

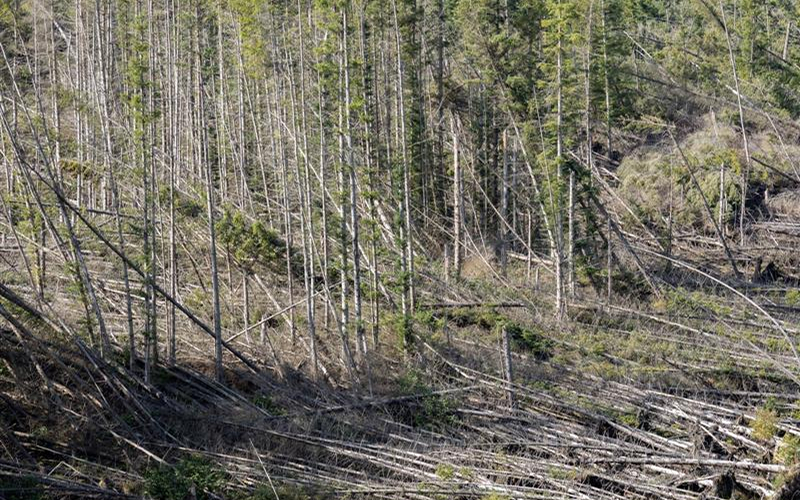
Planting woodland adjacent to established woodland or in large clumps is more likely to boost bird populations than random planting, modelling suggests.

Dr Bianca Ambrose-Oji will succeed Professor Chris Quine FRSE as Chief Scientist, following Professor Quine’s decision to retire from the role at the end of April 2025.
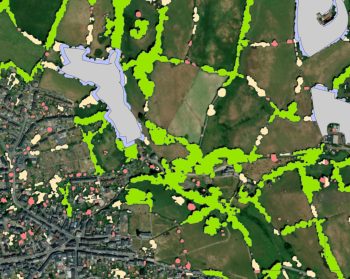
England’s non-woodland trees have been mapped for the first time, revealing these trees make up nearly one third of our nation’s tree cover.

A recent collaborative study with Edinburgh Napier University has identified underutilised species with promising timber potential to support future forestry needs.
Discover our Climate Change Hub, a comprehensive, evidence-based resource that brings together climate change adaptation advice for forest and woodland owners and managers in the UK.


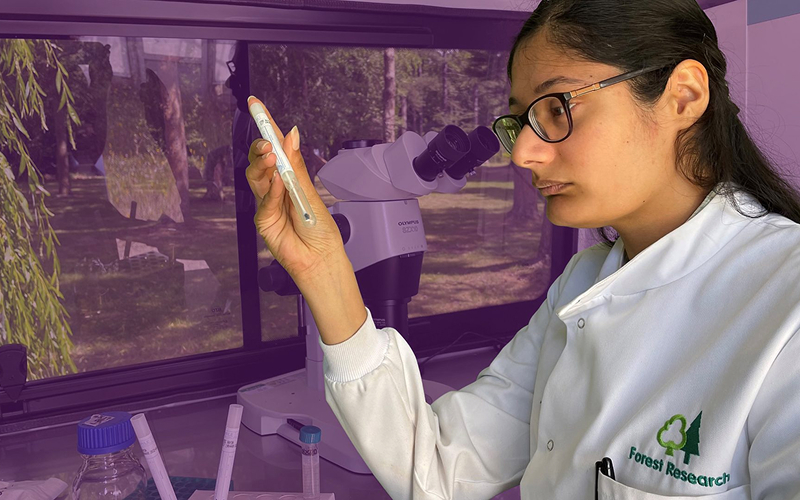
Imagine a job where every day is different, where science meets policy, and where your work makes a real impact. Mariella Marzano, Principal Social Scientist, tells us why she loves her role at Forest Research.

Matt Wilkinson explains how Forest Research's NCEA Programme is leading the way by using cutting-edge science to assess and protect England's ecosystems.

Tom Nisbet, Head of Physical Environmental Sciences, details how the new UKFS Practice Guide supports the creation and management of riparian woodlands to protect waterways and enhance biodiversity.

Stay ahead of the threat with TreeAlert’s new dashboard for real-time insights on tree pests and diseases across Great Britain.

Detection dogs have been used in the UK to successfully identify tree disease, helping track down the deadly tree pathogen Phytophthora ramorum.

Plan smarter, grow stronger. Senior Climate Change Scientist Tom Locatelli explains how ForestGALES helps foresters tackle wind risk and build resilient woodlands in Great Britain, and beyond.
Work at the cutting-edge of environmental science research with Forest Research, Great Britain’s leading organisation for forestry and tree-related research.

Learn how Ash Dieback is impacting Great Britain's native ash trees, and discover resources to help slow its spread.
Understand the threat of Oak Processionary Moth to the country’s oak trees and access key information on its management and control.
Explore this detailed resource with information on common tree pests and diseases, from Acute Oak Decline to the Asian Longhorn Beetle.
Access a detailed database on information on over 60 tree species that are either widely grown in British forests or which could play an increasing role in the future.
Explore ForestGALES, a computer tool that assesses wind damage risk to forests in Britain, allowing comparison of different silvicultural practices.
Discover vital insights about Britain’s woodlands through the National Forest Inventory (NFI), a comprehensive programme offering up-to-date data on forest size, distribution, health, and biodiversity.
We carry out research to develop a better understanding of the ways in which trees and woodlands can benefit society
Chemical analysis of plant, water and soil samples, testing of plant stock quality and tree assessment products
The Tree Health Diagnostic and Advisory Service provide advice and where possible diagnosis and identification of tree pest and pathogen
By analysis of DNA extracted from samples, Forest Research can identify the presence of cryptic or reclusive species.
The Land Use and Ecosystem Services Research Group provides services to the forestry and environment sectors.
Notifications