Summary
Alice Holt Forest is one of twelve sites, which currently make up the ECN terrestrial network and which operates to a uniform system of long term data collection of core measurements:
- Land use & site management: Vegetation cover at Alice Holt
- Meteorology
- Nitrogen dioxide
- Gaseous ammonia
- Precipitation chemistry
- Soil chemistry
- Soil solution chemistry
- Soil structure: Soil survey at Alice Holt
- Vegetation
- Invertebrates
- Moths
- Butterflies
- Spittle Bugs
- Ground Beetles
- Vertebrates
Environmental change network core measurements at Alice Holt Forest – Meteorology
Automatic measurements are all recorded at 5 second intervals and stored as hourly summaries. Manual measurements are made in accordance with standard Meteorological Office procedures.
- Wind Speed (m s-1)
- Wind Direction (degrees from N)
- Run of wind
- Wet bulb temperature (oC)
- Dry Bulb temperature (oC)
- Solar Radiation (W m-2)
- Albedo/sky (W m-2)
- Albedo/ground (W m-2)
- Rainfall (mm)
- Surface wetness (minutes per hour when surface is wet)
- Soil temperature 10 cm – under bare soil (°C)
- Soil temperature 30 cm – under grass (°C)
- Soil moisture (%)
Environmental change network core measurements at Alice Holt Forest – Precipitation chemistry
Measurements are taken weekly:
- Volume (mls)
- pH
- Conductivity (μS)
- Alkalinity (mg l-1)
- Sodium Na+ (mg l-1)
- Potassium K+ (mg l-1)
- Calcium Ca2+ (mg l-1)
- Magnesium Mg2+ (mg l-1)
- Iron Fe2+ (mg l-1)
- Aluminium Al3+ (mg l-1)
- Phosphate PO43--P (mg l-1)
- Ammonia NH4+-N (mg l-1)
- Chloride Cl– (mg l-1)
- Nitrate NO3–-N (mg l-1)
- Sulphate SO42--S (mg l-1)
Environmental change network core measurements at Alice Holt Forest – Soil chemistry
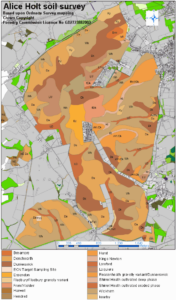
Soil survey and classification data
Baseline survey at 1:100000
Soil characterisation and change
Core sampling for major elements (five yearly):
- Horizon depth and thickness
- Soil moisture
- pH
- Exchangeable:
- Acidity
- Sodium
- Potassium
- Calcium
- Magnesium
- Manganese
- Aluminium
- Total:
- Nitrogen
- Phosphorus
- Sulphur
- Organic Carbon
- Inorganic Carbon
- Soil archiving
See:
Benham, S.E., Vanguelova, E. I. and Pitman, R.M. (2012). Short and long term changes in carbon, nitrogen and acidity in the forest soils under oak at the Alice Holt Environmental Change Network site. Science of the Total Environment. 421-422.
Profile sampling and description (20 yearly)
- Slope/aspect
- Altitude
- Land use
- Horizon Depth
- Particle size analysis
- Soil mineralogy
- Bulk density
- Soil water release
- Soil moisture
- pH
- Exchangeable:
- Acidity
- Sodium
- Potassium
- Calcium
- Magnesium
- Manganese
- Aluminum
- Total:
- Nitrogen
- Phosphorus
- Sulphur
- Organic Carbon
- Inorganic Carbon
- Lead
- Zinc
- Cadmium
- Copper
- Mercury
- Cobalt
- Molybdenum
- Arsenic
- Chromium
- Nickel
- Extractable:
- Iron
- Aluminium
- Phosphorus
Environmental change network core measurements at Alice Holt Forest – Soil solution chemistry
Soil solution samples are collected using twelve Prenart ‘super quartz’ soil water samplers. Six samplers are installed in the A horizon and six at the base of the B horizon. Each sample is analysed for:
- Volume (mls)
- Vacuum (bars)
- pH
- Conductivity (μS)
- Alkalinity (mg l-1)
- Sodium Na+ (mg l-1)
- Potassium K+ (mg l-1)
- Calcium Ca2+ (mg l-1)
- Magnesium Mg2+ (mg l-1)
- Iron Fe2+ (mg l-1)
- Aluminium Al3+ (mg l-1)
- Phosphate PO43--P (mg l-1)
- Ammonia NH4+-N (mg l-1)
- Chloride Cl– (mg l-1)
- Nitrate NO3–-N (mg l-1)
- Sulphate SO42--S (mg l-1)
- Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC)
Environmental change network core measurements at Alice Holt Forest – vegetation
Baseline survey data (once only)
300 systematically-chosen plots (2 m x 2 m) covering the whole site. Species presence recorded then related to National Vegetation Classification (NVC).

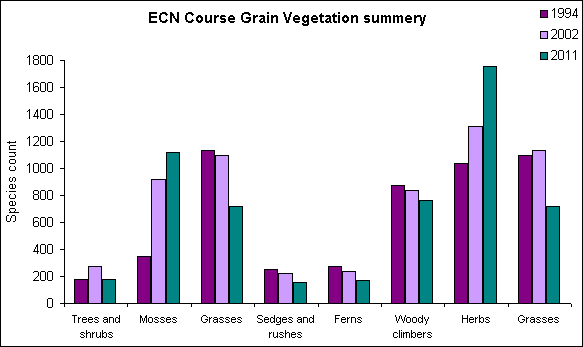
Coarse-grain (every nine years)
50 randomly chosen plots from the original baseline survey:
- Altitude
- Aspect
- Slope form
- Land use
- Biotic effects
- Species presence
- Seedling counts
- Tree growth (height and diameter)
- Stand structure
- Linear features
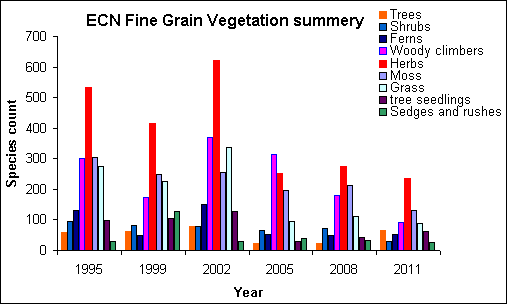
Fine grain (every three years)
50 plots located randomly within the NVC identified by the baseline survey:
- Species presence
- Physical features
- Biotic features
Environmental Change Network core measurements at Alice Holt Forest – butterflies
Butterflies are biologically suitable as indicator species, having rapid lifecycles and, in many cases, high sensitivity to environmental conditions allow us to assess the impacts of climate change.
The UK butterfly monitoring scheme transect method, involves weekly butterfly counts along fixed routes throughout the season. These species counts generate annual site abundance indices.
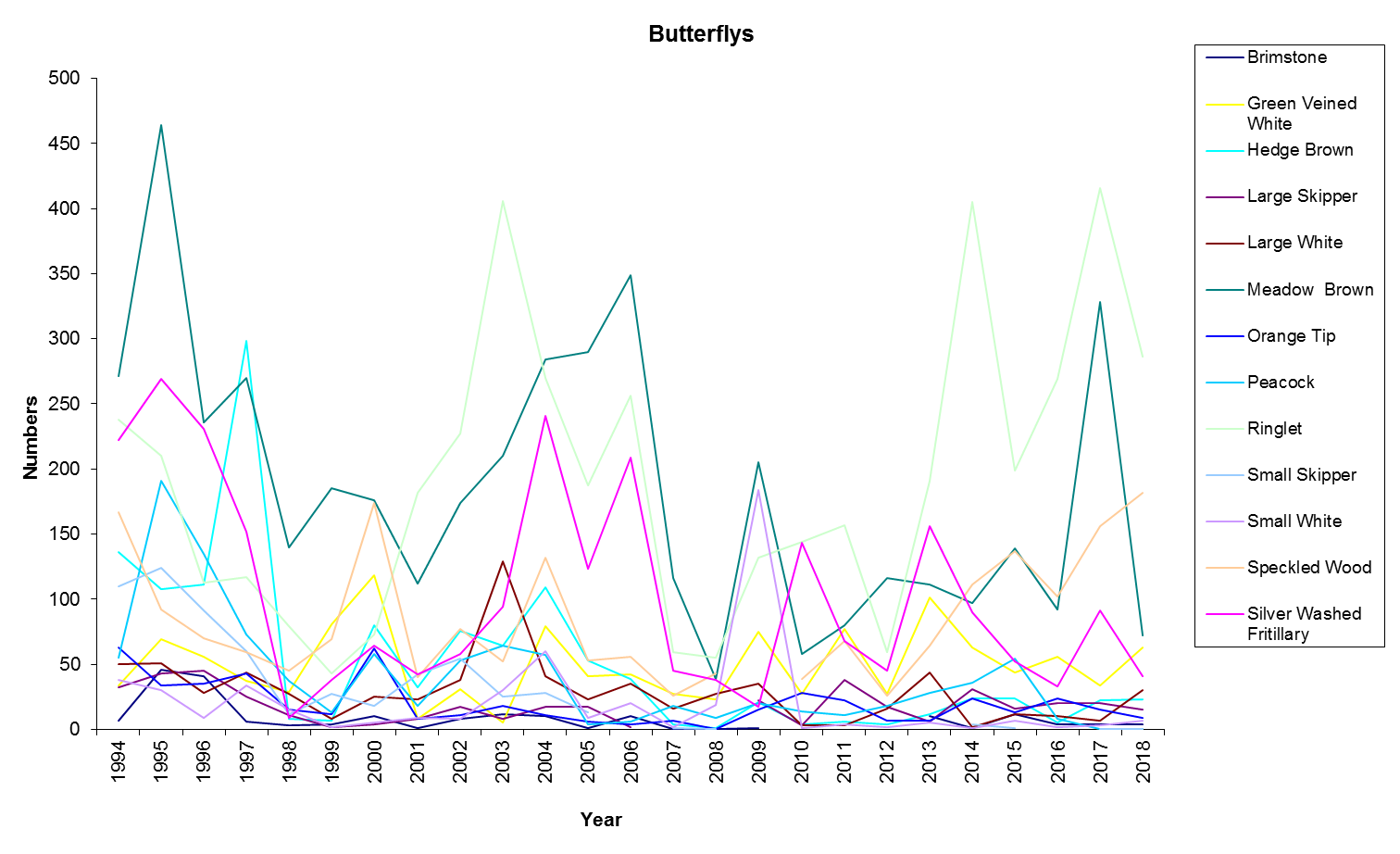 |
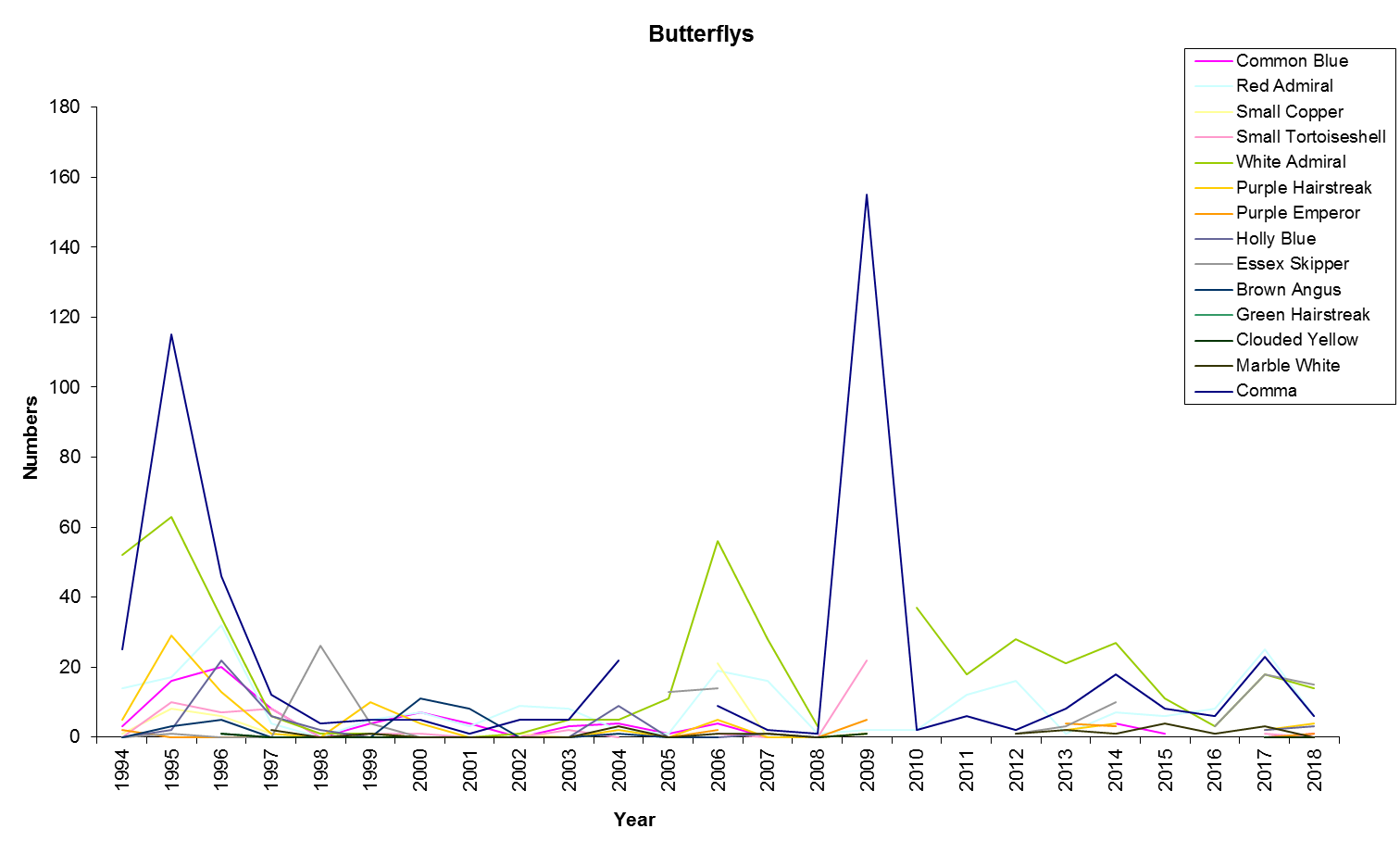 |
Results are split over two graphs for clarity.
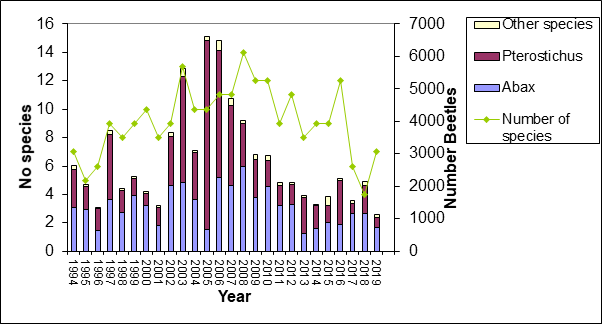
Environmental Change Network core measurements at Alice Holt Forest – ground beetles
Ground Beetles (Carabidae) can be used to demonstrate changes in prey invertebrates. At Alice Holt the majority of beetles found are Abax parallelepipedus and Pterostichus madidus. Although variable year on year their populations have remained relatively stable. Species associated with dead wood and damp conditions (Cychrus caraboides, Nebria brevicollis) have increased significantly most likely due to increases in litter accumulation (evident from the soil survey) dead wood, and shade associated with natural stand ageing.
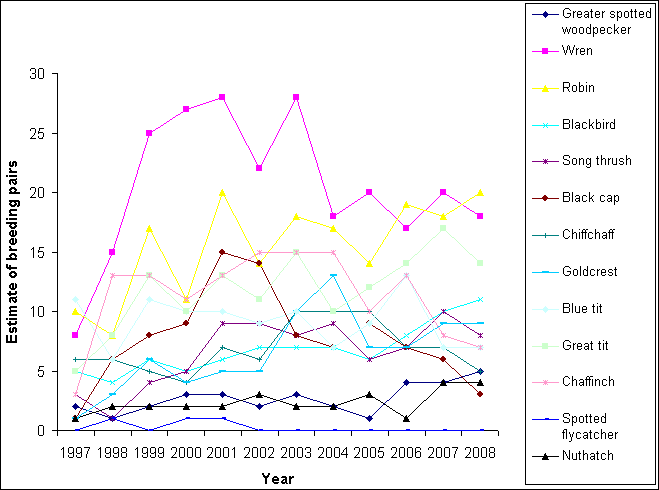
Environmental Change Network core measurements at Alice Holt Forest – bird population (CBS)
Bird populations are recognised as a reliable indicator of the general environment. In general populations at Alice Holt are decreasing. Predations of eggs by increasing squirrel populations and the removal of the shrub layer by grazing deer have a negative effect whilst milder winters increase survival chances.
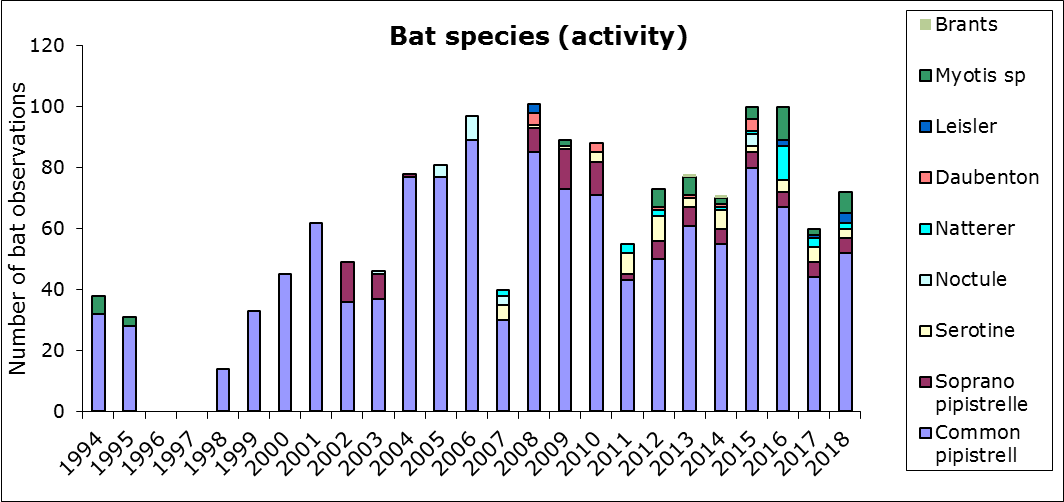
Environmental Change Network core measurements at Alice Holt Forest – bats
Nine species of UK bat are known to use the site, the most common species being the common pipistrelle whose numbers show an increasing trend over time.